The rules of digital visibility have fundamentally changed. As AI-powered search becomes the dominant discovery channel, the question is no longer just “how do I rank?” but “how do I get mentioned by AI?” This comprehensive analysis synthesizes the latest academic research, proprietary industry data analyzing 680 million+ citations, and platform documentation to provide actionable intelligence for digital marketing professionals navigating this rapidly evolving landscape. By the end of this report, you’ll understand exactly how LLMs select sources to cite, which signals matter most (spoiler: it’s not backlinks), and what data-backed strategies actually increase AI visibility.
Executive Summary: The New Rules of AI Visibility
TL;DR:
- Brand search volume (not backlinks) is the #1 predictor of LLM citations (0.334 correlation)
- Sites on 4+ platforms are 2.8x more likely to appear in ChatGPT responses
- Princeton GEO research shows optimization can boost AI visibility by 30-40%
- Only 11% of domains are cited by BOTH ChatGPT and Perplexity
- Wikipedia content represents ~22% of major LLM training data
- Adding statistics increases AI visibility by 22%; quotations by 37%
The emergence of AI-powered search has fundamentally transformed how brands achieve visibility online. As ChatGPT processes 3+ billion prompts monthly, Perplexity indexes 200+ billion URLs, and Google AI Overviews appear in 13%+ of searches, digital marketers must adapt to an entirely new set of ranking signals.
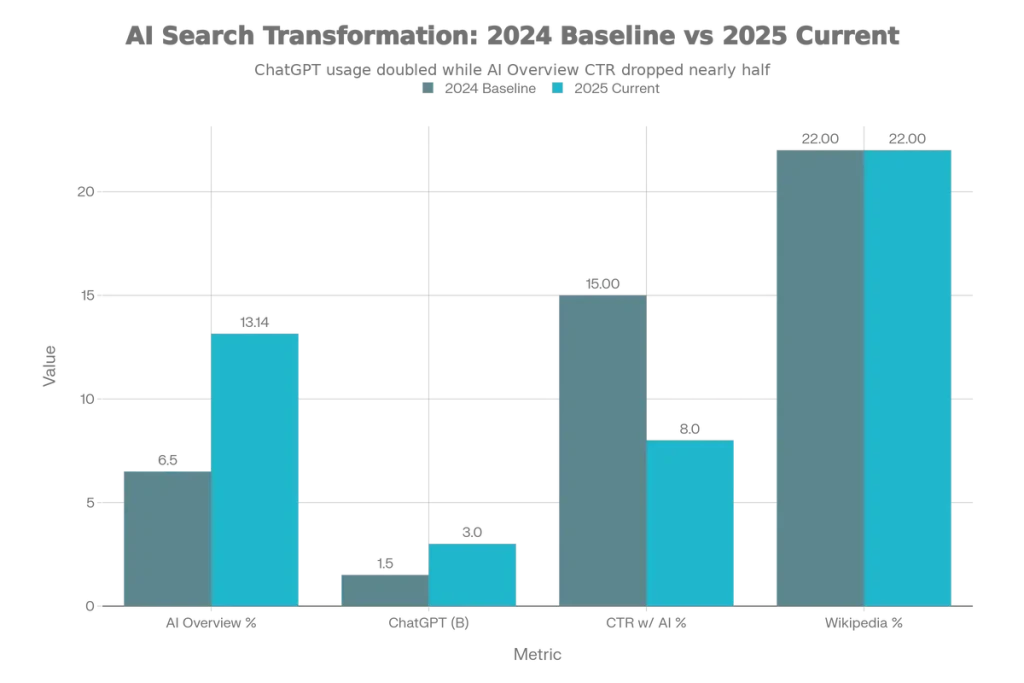
| Metric | 2024 Baseline | 2025 Current | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Overview Appearance Rate | 6.49% | 13.14% | +102% |
| ChatGPT Monthly Prompts | ~1.5B | 3B+ | +100% |
| CTR with AI Overviews | 15% | 8% | -47% |
| Cross-platform Citation Overlap | N/A | ~11% | Low overlap |
| Wikipedia Share of Training Data | ~22% | ~22% | Stable |
For a detailed breakdown of these unprecedented shifts, explore our comprehensive 2025 organic search crisis analysis.
How LLMs Retrieve and Select Sources
TL;DR:
- Two knowledge pathways: Parametric (training data) vs. Retrieved (real-time RAG)
- 60% of ChatGPT queries answered from parametric knowledge alone
- RAG uses hybrid retrieval: semantic search + BM25 keyword matching
- Hybrid retrieval delivers 48% improvement over single-method approaches
- Page-level chunking achieves 0.648 accuracy with lowest variance (NVIDIA)
Understanding how AI systems select sources requires distinguishing between two fundamentally different knowledge pathways that operate in all major LLMs:
Parametric Knowledge (Training Data)
Parametric knowledge represents everything an LLM “knows” from pre-training. This knowledge is static, fixed at the model’s training cutoff, and accessed in milliseconds without external calls. Entities mentioned frequently across authoritative sources during training develop stronger neural representations, making them more likely to be recalled.
22% of training data for major AI models comes from Wikipedia content.
60% of ChatGPT queries are answered purely from parametric knowledge without triggering web search.
Retrieved Knowledge (RAG Systems)
Retrieved knowledge through RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) operates through a structured pipeline that modern AI search systems use to access current information:
- Query Encoding: User queries converted to vector embeddings (e.g., OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-large uses 3,072 dimensions)
- Hybrid Retrieval: Combines semantic search (dense vectors) with keyword matching (BM25) using Reciprocal Rank Fusion
- Reranking: Cross-encoder models evaluate query-document pairs jointly, improving NDCG@10 by 28%
- Generation: Top 5-10 retrieved chunks injected into LLM prompt as context
Content Chunking: Why Structure Matters
How content is chunked significantly impacts what gets retrieved. NVIDIA benchmarks demonstrate that page-level chunking achieves 0.648 accuracy with the lowest variance. For practitioners, this means structuring content so individual paragraphs (200-500 words) can stand alone as citable units—each semantic chunk should comprehensively answer a potential query. This immediate utility is precisely what drives success in AI Overviews; understanding how to optimize for these direct answers is covered in a dedicated zero-click marketing guide.
Platform-by-Platform Citation Analysis
TL;DR:
- ChatGPT: 87% of citations match Bing’s top 10; Wikipedia dominates at 47.9%
- Perplexity: Reddit leads at 46.7%; indexes 200B+ URLs in real-time
- Google AI Overview: 93.67% cite at least one top-10 organic result
- Claude: Brave Search backend; Constitutional AI favors trustworthy sources
- Microsoft Copilot: IndexNow critical for instant Bing indexing
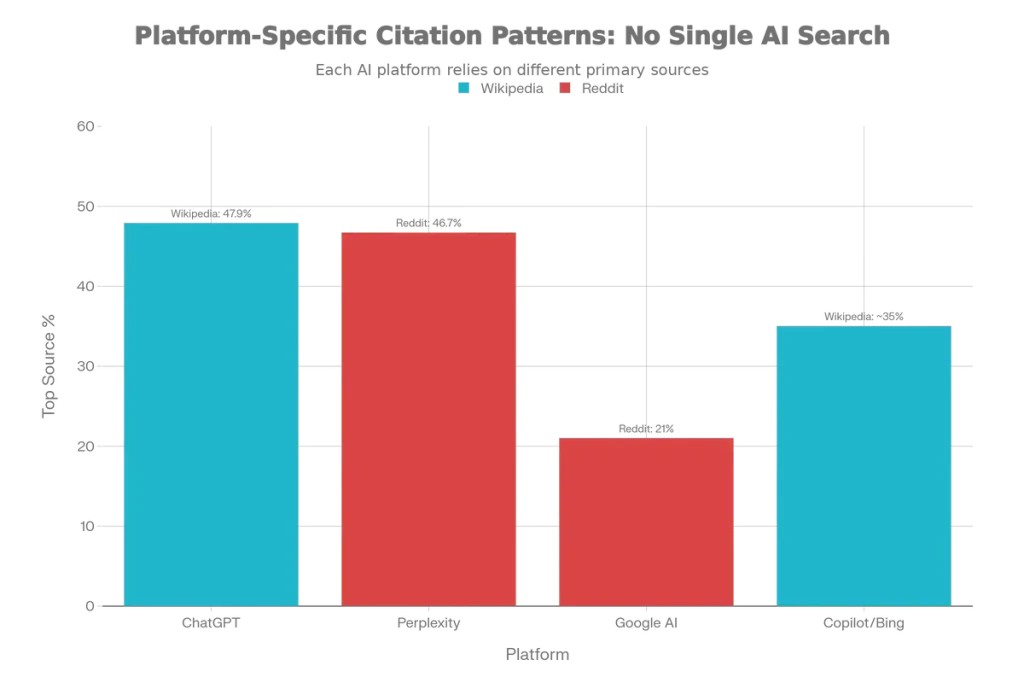
| Platform | Top Source | % of Citations | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Wikipedia | 47.9% | Training data dominant |
| Perplexity | 46.7% | Real-time retrieval | |
| Google AI Overview | 21% | Most diversified | |
| Copilot/Bing | Wikipedia | ~35% | Bing grounding |
ChatGPT: Wikipedia Dominance & Bing Correlation
ChatGPT operates in two distinct modes. Without web browsing enabled, responses draw exclusively from parametric knowledge—entity mentions depend entirely on training data frequency. OpenAI’s training data hierarchy prioritizes:
- Tier 1: Wikipedia, licensed publisher partners (Condé Nast, Vox Media), GPTBot-accessible sites
- Tier 2: Reddit content with 3+ upvotes, industry publications
- Tier 3: YouTube transcripts, podcasts
When web browsing is enabled, ChatGPT queries Bing and selects 3-10 diverse sources. Seer Interactive’s analysis of 500+ citations found that 87% of SearchGPT citations match Bing’s top 10 organic results, with only 56% correlation with Google results.
3.2x more often ChatGPT mentions brands than it actually cites them with links.
Perplexity: Real-Time Retrieval with Reddit Emphasis
Perplexity represents a fundamentally different architecture: every query triggers real-time web search against a proprietary index of 200+ billion URLs, processed at tens of thousands of indexing operations per second across 400+ petabytes of storage.
| Source Type | % of Top 10 Citations |
|---|---|
| 46.7% | |
| YouTube | 13.9% |
| Gartner | 7.0% |
| Typical response | 5-10 inline citations |
Google AI Overview: Traditional Signals Plus Diversification
Google AI Overview maintains the strongest correlation with traditional search rankings—93.67% of citations link to at least one top-10 organic result. However, only 4.5% of AI Overview URLs directly matched a Page 1 organic URL, suggesting Google draws from deeper pages on authoritative domains.
10.2 average links from 4 unique domains per AI Overview response.
50%+ of searches now show AI Overviews (up from 18% in March 2025).
Claude & Microsoft Copilot
Claude’s knowledge retrieval is shaped by Anthropic’s Constitutional AI framework, creating strong preferences for helpful, harmless, and honest content. When using web search (powered by Brave Search), Claude autonomously determines search necessity and provides citations with URL, title, and cited_text snippets.
Microsoft Copilot uses a multi-layer architecture with Bing grounding for consumer queries. IndexNow becomes critical for Copilot visibility—this open protocol enables instant content indexing notification to Bing, adopted by Amazon, Shopify, GoDaddy, and Internet Archive.
What the Research Reveals About Citation Signals
TL;DR:
- Brand search volume has 0.334 correlation with AI visibility (strongest predictor)
- Backlinks show weak or neutral correlation—contradicting traditional SEO wisdom
- GEO methods boost visibility by up to 40% (Princeton study, 10K queries)
- Adding citations: 115.1% visibility increase for sites ranked 5th
- Statistics addition: 22% improvement; Quotations: 37% improvement
- 65% of AI bot hits target content published within the past year
The Princeton GEO Study: Foundational Findings
The seminal “GEO: Generative Engine Optimization” paper from Princeton University (published KDD 2024, analyzing 10,000 queries across 9 sources) established several counterintuitive findings that challenge traditional SEO assumptions:
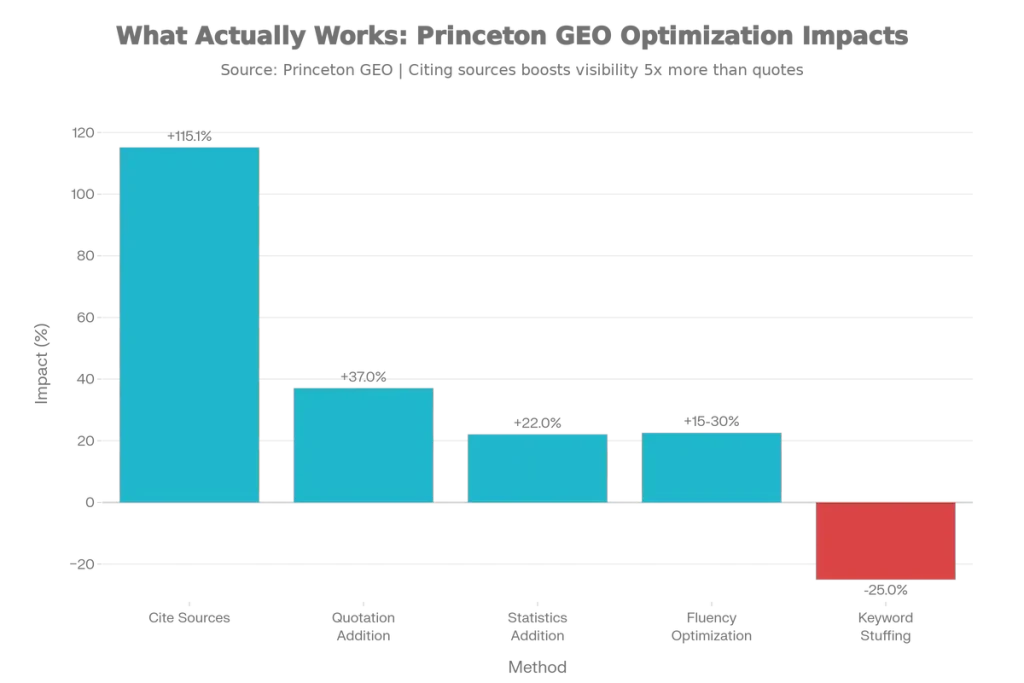
| Optimization Method | Visibility Impact |
|---|---|
| Cite Sources Method | 115.1% increase (for rank #5 sites) |
| Quotation Addition | 37% improvement (Perplexity) |
| Statistics Addition | 22% improvement |
| Fluency Optimization | 15-30% visibility boost |
| Keyword Stuffing | NEGATIVE impact |
Critical insight: Lower-ranked traditional SERP sites benefit significantly more from GEO optimization than top-ranked sites—making this a particularly powerful strategy for challengers competing against established players.
The 7,000-Citation Analysis: Brand Search Volume Wins
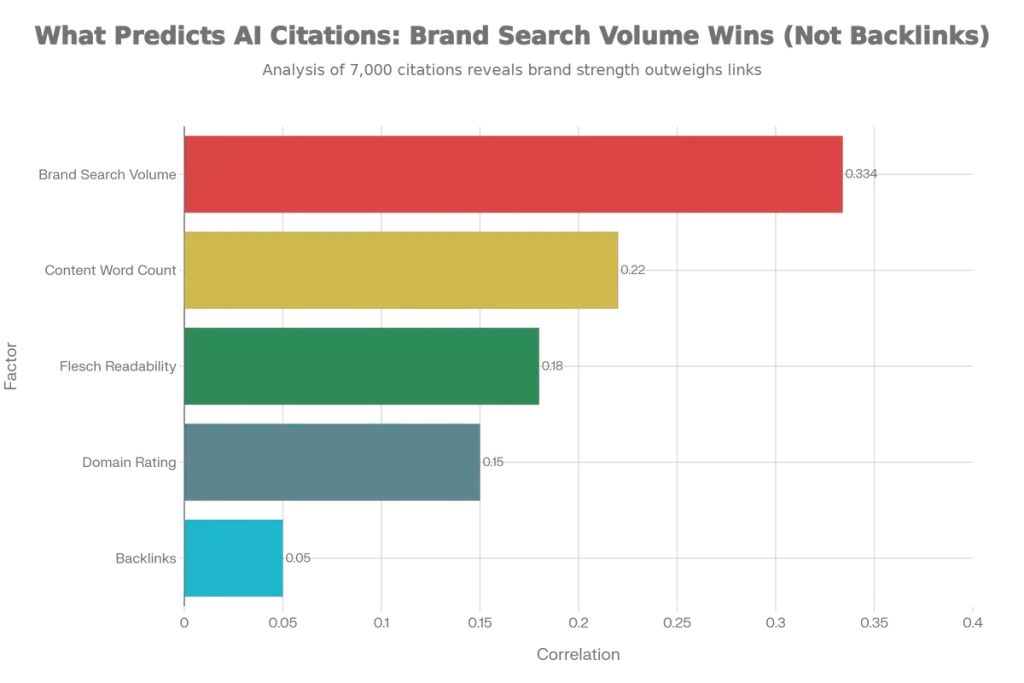
Research analyzing 7,000+ citations across 1,600 URLs produced critical insights that contradict decades of traditional SEO wisdom:
| Factor | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Brand Search Volume | 0.334 (STRONGEST) |
| Content Word Count | Higher for Perplexity/AIOs |
| Domain Rating | Light preference for ChatGPT |
| Flesch Readability Score | Matters for ChatGPT |
| Backlinks | WEAK or NEUTRAL |
The backlink finding contradicts decades of traditional SEO wisdom. An article with 10,000+ words and Flesch Score 55 received 187 total citations (72 from ChatGPT), while similar content under 4,000 words with lower readability received only 3 citations.
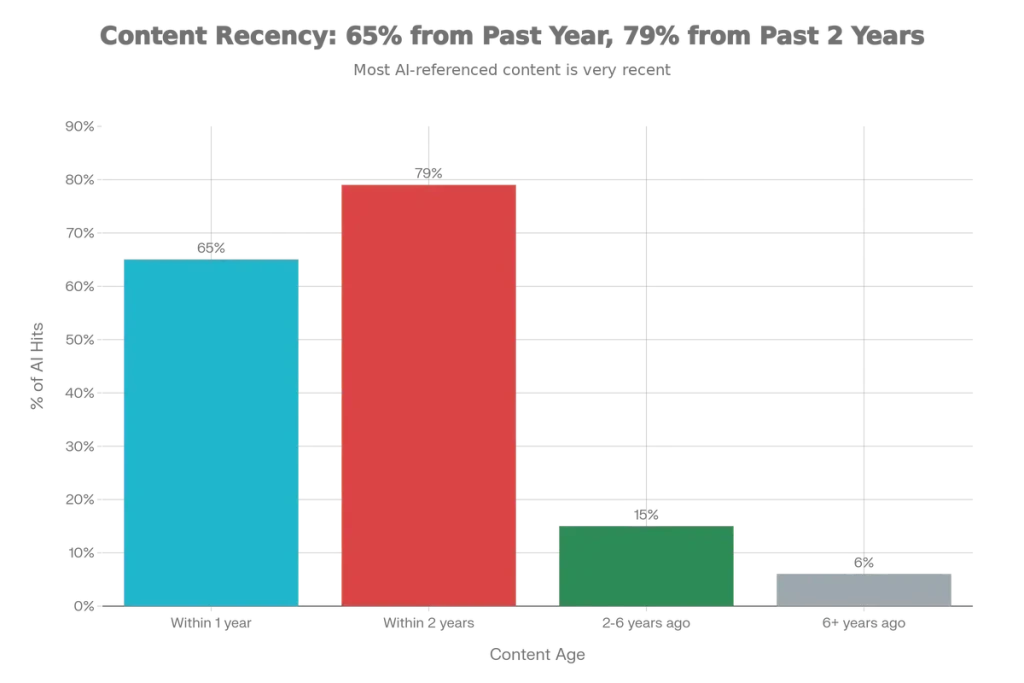
Content Recency Research
Analysis of 300,000+ keywords and 5,000+ URLs revealed critical insights about content freshness:
-
- 65% of AI bot hits target content published within the past year
- 79% from content updated within 2 years
- Only 6% from content older than 6 years
- Multi-modal content (images, videos) did NOT move the needle
- Google Page 1 rankings correlate ~0.65 with LLM mentions
Structured Data & Schema Markup Impact
TL;DR:
- Well-implemented schema: Rank 3 + AI Overview appearance
- No schema: Not indexed at all (Search Engine Land experiment)
- Comparison tables with proper HTML: 47% higher AI citation rates
- FAQPage schema directly feeds AI question-answer extraction
- Wikidata is #1 source for Google’s Knowledge Graph (500B facts, 5B entities)
- sameAs property linking to Wikidata increases entity recognition
Schema Markup’s Documented Impact
A Search Engine Land experiment tested three identical single-page sites differing only in schema quality, with dramatic results:
| Schema Quality | Google Rank | AI Overview |
|---|---|---|
| Well-implemented | Position 3 | YES – Appeared |
| Poorly implemented | Position 8 | No appearance |
| No schema | NOT INDEXED | N/A |
47% higher AI citation rates for comparison tables using proper <thead> and descriptive columns.
Priority Schema Types for AI Visibility
Tier 1 — Essential:
- HowTo: Enables step extraction for procedural queries
- Article/BlogPosting: Establishes content type and freshness
- Organization: Brand recognition and authority signals
- Person: E-E-A-T signals and author authority
Tier 2 — High Value:
- Product/Offer: Pricing and availability for AI shopping queries
- LocalBusiness: NAP clarity for location queries
- Review/AggregateRating: Trust signals for recommendations
- Speakable: Voice assistant optimization
Entity Optimization: Why Wikidata Matters
Wikidata serves as the #1 source for Google’s Knowledge Graph (500 billion facts about 5 billion entities). Creating or optimizing a Wikidata entry requires essential properties: Label, Description, Aliases, Industry, Founded date, HQ, and Website.
2.8x more likely to appear in ChatGPT responses when brand is mentioned on 4+ platforms.
Content Architecture for Maximum Citations
TL;DR:
- Lead with the answer: First paragraph must directly address the query
- Optimal paragraph length: 40-60 words for easy AI extraction
- Comparative listicles: 32.5% of all AI citations (highest performer)
- Self-contained sections that work as standalone chunks
- Clear heading hierarchy mirroring likely search queries
- Include verifiable data points with proper citations
Structure for RAG Retrieval Success
The Princeton GEO research and industry studies converge on specific content patterns that maximize AI citation probability:
- Lead with the answer: “The best X is Y” not “Y might be good”
- Optimal paragraph length: 40-60 words for easy AI extraction and chunking
- Clear heading hierarchy: H2/H3 headings that mirror likely search queries
- Self-contained sections: Each section independently comprehensible when extracted as a chunk
- Verifiable data points: Statistics addition showed 22% visibility improvement
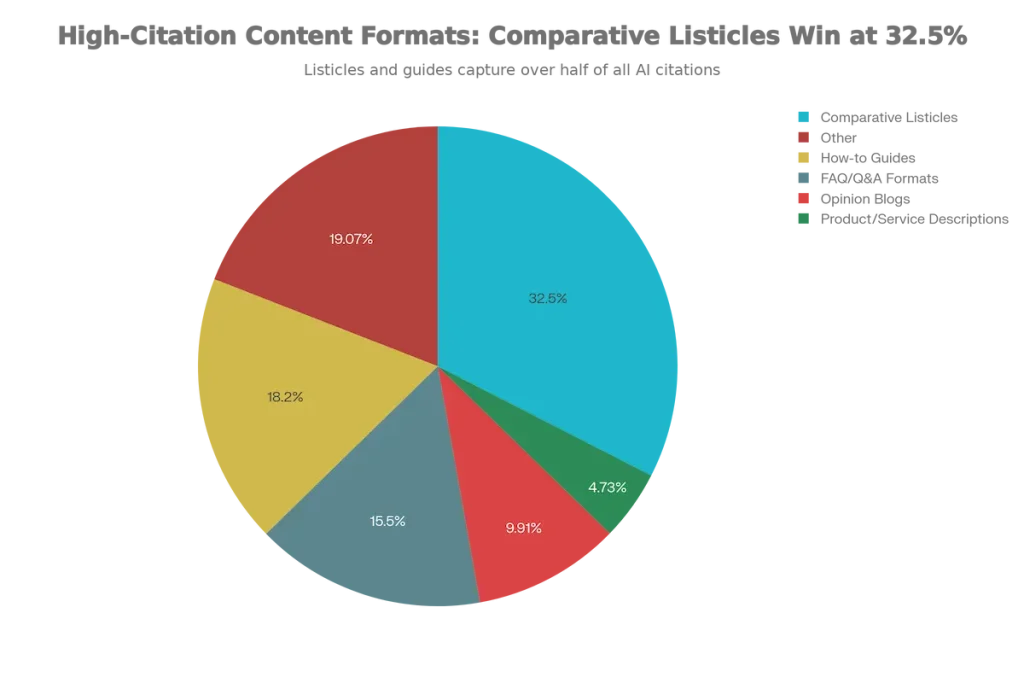
High-Citation Content Formats
Analysis of 30M+ citations reveals dramatic differences in format performance:
| Content Format | % of AI Citations |
|---|---|
| Comparative Listicles | 32.5% (HIGHEST) |
| Opinion Blogs | 9.91% |
| Product/Service Descriptions | 4.73% |
| FAQ/Q&A Formats | High (Perplexity/Gemini) |
| How-to Guides | Strong performer |
Technical SEO for AI Crawler Access
TL;DR:
- GPTBot traffic grew 305% from May 2024-2025
- 312 of top 10K domains block GPTBot entirely; 546 have explicit AI bot rules
- IndexNow critical for Bing/Copilot visibility (instant indexing)
- Different bots for training vs. search: OAI-SearchBot vs. GPTBot
- Allow search-focused bots while potentially blocking training-only bots
- Fast page load times favor AI crawler access
AI Crawler Landscape
| Crawler | Owner | Purpose | Robots.txt Token |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Model training | GPTBot |
| OAI-SearchBot | OpenAI | Real-time search | OAI-SearchBot |
| Google-Extended | Gemini training | Google-Extended |
|
| ClaudeBot | Anthropic | Model training | ClaudeBot |
| PerplexityBot | Perplexity | Real-time search | PerplexityBot |
| Applebot-Extended | Apple | Apple Intelligence | Applebot-Extended |
305% growth in GPTBot traffic from May 2024-2025.
Strategic Robots.txt Configuration
For maximum visibility, allow search-focused bots while potentially blocking training-only bots:
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Allow: /
User-agent: PerplexityBot
Allow: /
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: / # Optional: block training but allow searchInfrastructure Requirements
- IndexNow implementation for Bing/Copilot visibility (instant indexing)
- Fast page load times (crawlers favor performant sites)
- Mobile-first optimization (majority of AI Overview citations from mobile-indexed pages)
- JSON-LD structured data (Google’s preferred format)
- Semantic HTML5 markup (header, nav, main, article, footer, time tags)
Yet even the best-structured content won’t get cited if the underlying page has technical SEO problems – slow load times, broken canonicals, or misconfigured schema. Before investing in AI citation strategy, run a baseline SEO audit on every page to eliminate the technical friction that prevents both crawlers and LLMs from trusting your content.
Measurement Frameworks & Tracking Tools
TL;DR:
- Share of Voice (SOV): Top brands capture ≥15%, enterprise leaders reach 25-30%
- Citation Drift: Google AI Overviews 59.3% monthly; ChatGPT 54.1%
- Enterprise tools: Profound (240M+ citations), Semrush AI Toolkit
- Mid-market: LLMrefs, Peec AI (€89-€499/month), First Answer
- Budget options: Otterly.AI, Scrunch AI, Knowatoa (freemium)
- Track: Brand mentions, citation frequency, sentiment, competitive position
Key Metrics for AEO Performance
| Metric | Definition | Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Share of Voice | % of AI answers mentioning your brand vs. competitors | ≥15% (top brands) |
| Citation Frequency | How often URLs are cited across platforms | Track monthly |
| Brand Sentiment | Positive/negative/neutral characterization | >70% positive |
| Citation Drift | Monthly volatility in citations | ~55% normal |
Tool Landscape by Investment Tier
Enterprise ($400+/month):
- Profound: 240M+ ChatGPT citations tracked, competitive benchmarking, GA4 integration
- Semrush AI Toolkit: Integrated with existing SEO suite
- Goodie AI: End-to-end platform with attribution
Mid-Market ($50-400/month):
- LLMrefs: Keyword-to-prompt mapping, share of voice tracking
- Peec AI: Clean UI, prompt-level reporting (€89-€499/month)
- First Answer: Cross-platform tracking (“GA for AI Search”)
Budget ($30-50/month):
- Otterly.AI: Domain citations, GEO audits, alerts
- Scrunch AI: Brand mentions, competitive analysis
- Knowatoa: Historical data, freemium tier
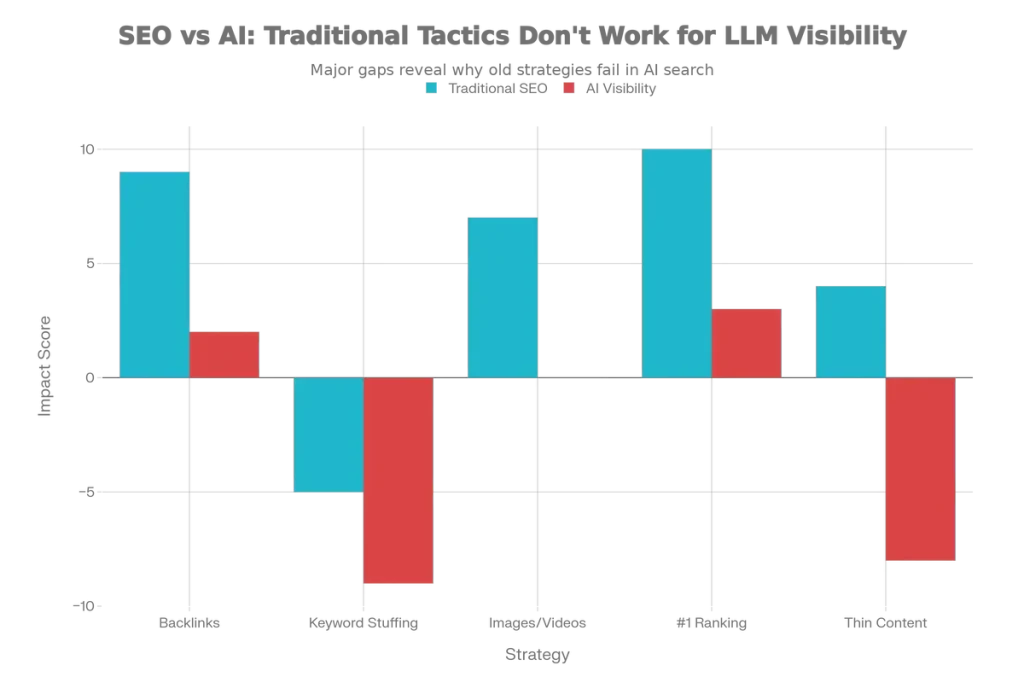
What Doesn’t Work: Common Misconceptions
TL;DR:
- Backlink quantity: Weak/neutral correlation with AI citations
- Keyword stuffing: Performs WORSE in generative engines (Princeton)
- Multi-modal content variety: Images/videos didn’t move the needle
- Position #1 ranking: Only 4.5% of AI Overview URLs matched #1 organic
- Short-form thin content: AI prefers comprehensive, synthesizable content
- Traditional SEO signals alone are insufficient for AI visibility
Research reveals several surprising findings that contradict traditional SEO assumptions:
| Strategy | Traditional SEO Impact | AI Visibility Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Backlink quantity | HIGH (core signal) | WEAK/NEUTRAL |
| Keyword stuffing | Negative | WORSE in AI |
| Images/videos | Engagement boost | No measurable impact |
| #1 ranking focus | Primary goal | Only 4.5% correlation |
| Thin content at scale | Variable | Actively penalized |
The key insight: AI systems prioritize brand authority and content comprehensiveness over traditional link-based signals. Quality and depth trump quantity.
Implementation Roadmap
TL;DR:
- Phase 1 (Weeks 1-4): Foundation — robots.txt, schema, Wikidata, monitoring
- Phase 2 (Weeks 5-12): Content optimization — structure, statistics, listicles
- Phase 3 (Ongoing): Entity building — Wikipedia, Reddit, cross-platform presence
- Priority: Brand-building activities now directly impact AI visibility
- Monitor citation drift monthly (40-60% normal volatility)
- Measure success by AI visibility metrics, not just traditional rankings
Phase 1: Foundation (Weeks 1-4)
- Audit and configure robots.txt for AI crawler access
- Implement Organization, Person, and FAQPage schema
- Create or verify Wikidata entry with sameAs links
- Configure GA4 for AI traffic attribution (perplexity.ai, chat.openai.com referrals)
- Select and deploy AEO monitoring tool
Phase 2: Content Optimization (Weeks 5-12)
- Restructure high-value content with direct answers in opening paragraphs
- Add statistics, citations, and expert quotations to key pages
- Create comparative listicles for target topics (32.5% of AI citations)
- Implement HowTo schema for procedural content
- Ensure 40-60 word paragraphs for optimal chunking
Phase 3: Entity Building (Ongoing)
- Build Wikipedia presence if meeting notability guidelines
- Engage authentically on Reddit in relevant subreddits
- Pursue placements on frequently-cited platforms (Forbes, G2, industry publications)
- Create YouTube content with optimized descriptions/transcripts
- Monitor and respond to citation drift monthly
Conclusion: The strategic shift from keywords to entities
The transition from traditional SEO to AEO represents a fundamental shift in how digital visibility is achieved. Brand search volume—not backlinks—is the strongest predictor of AI citations (0.334 correlation). This means brand-building activities that seemed disconnected from SEO now directly impact AI visibility.
The platforms diverge significantly: ChatGPT relies heavily on Wikipedia and parametric knowledge, Perplexity emphasizes real-time Reddit content, Google AI Overviews favor diversified cross-platform presence. Cross-platform optimization is essential—only 11% of domains are cited by both ChatGPT and Perplexity.
Three High-Leverage Actions:
- Establish entity presence on Wikidata, Wikipedia (if notable), and across 4+ third-party platforms (2.8x citation likelihood increase)
- Structure content for chunk extraction—lead with direct answers, use 40-60 word paragraphs, add statistics and citations (up to 40% visibility boost)
- Monitor platform-specific patterns—the 40-60% monthly citation drift means ongoing optimization is required
The practitioners who succeed in this environment will be those who shift focus from optimizing individual pages for keyword rankings to building comprehensive entity authority that AI systems recognize across their training data and real-time retrieval systems.
References
Academic Research & Studies
- GEO: Generative Engine Optimization (Princeton/KDD 2024)
- GEO: Generative Engine Optimization – OpenReview
- Generative Engine Optimization – Wikipedia
Industry Research & Data Analysis
- AI Visibility: How to Track & Grow Your Brand Presence in LLMs – Semrush
- STUDY: What Drives Brand Mentions in AI Answers? – Seer Interactive
- How to Get Your Brand in ChatGPT’s Training Data – Seer Interactive
- Study: AI Brand Visibility and Content Recency – Seer Interactive
- AI Platform Citation Patterns – Profound
- What is Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)? – Profound
- What content works well in LLMs? – Kevin Indig
- The State of AI Chatbots and SEO – Kevin Indig
- Google search rankings correlate with ChatGPT mentions – Search Engine Land
- 10 Data-Backed Strategies for LLM Visibility – Troy Van Camp
Schema & Structured Data
- Schema and AI Overviews: Does structured data improve visibility? – Search Engine Land
- Schema Markup for AI: The Tags That Help You Get Pulled – The HOTH
- Role of Schema Markup in Answer Engine Optimization – SEOTuners
- What is the Knowledge Graph? – Search Engine Land
- How Google’s Knowledge Graph works – Google Support
Platform Documentation
- AI Features and Your Website – Google Search Central
- Architecting and Evaluating an AI-First Search API – Perplexity Research
- Web search tool – Claude Docs
- How up-to-date is Claude’s training data? – Anthropic
- Claude Models Overview – Anthropic
- How Microsoft AI makes Bing and Copilot work – TechFinitive
GEO & AEO Strategy Guides
- Generative Engine Optimization framework introduced – Search Engine Land
- What is generative engine optimization (GEO)? – Search Engine Land
- What’s Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) & How To Do It – Foundation Inc
- How GEO Rewrites the Rules of Search – Andreessen Horowitz
- Generative engine optimization: What we know so far – HubSpot
- AI SEO: How Brand Mentions & Citations Drive LLM Visibility – Connective Web Design
- How to Earn LLM Citations – Ahrefs
- How to Earn LLM Citations To Build Authority – Awisee
- 7 Large Language Model Optimization Strategies – Surfer
Platform-Specific Optimization
- ChatGPT search vs. Google: How do they differ? – TechTarget
- ChatGPT Brand Mentions vs. Citations – BrightEdge
- Can PR improve a brand’s visibility in ChatGPT? – Cloudnine PR
- How to Get Indexed In Perplexity AI – WebFX
- Perplexity AI Optimization: How to Get Cited & Rank – OSP
- How To Get Your Content Cited by Claude AI – eSEOspace
- Google AI Overview and SEO Optimization – Cension AI
- Search Generative Experience (SGE) Statistics – SEO.AI
Tracking & Measurement Tools
- Ultimate Guide to LLM Tracking and Visibility Tools 2025 – Nick Lafferty
- Profound Review: Best AEO/GEO Platform for AI Search – Nick Lafferty
- 5 AI Visibility Tools to Track Your Brand Across LLMs – Backlinko
- 9 Best AI Search Visibility Tracking Tools – Rank Prompt
- 22 Best AI Search Rank Tracking & Visibility Tools – Rankability
- 8 Best Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) Tools – Writesonic
- LLMrefs – Generative AI Search Analytics
- AI Search Optimization: ChatGPT, Google & Perplexity Guide – Beauxhaus
Additional Resources
- Do More G2 Reviews Mean More AI Visibility? – G2
- Getting Cited in LLMs: A Guide to LLM Seeding – Pro Real Tech
- AI Search Optimization: Insights from 41M Results – SEOmator
- Webinar: ChatGPT vs. Google with Kevin Indig – AirOps
- How to Use Claude Web Search API – Apidog
- Parametric vs. Non-Parametric Memory in LLMs – Medium
Published December 2025. Updated quarterly with new insights.

