The year 2025 has brought unprecedented disruption to organic search traffic, with the majority of content publishers experiencing significant declines while total search volume paradoxically continues to grow. This comprehensive analysis examines traffic changes across major websites, quantifies the impact of AI-powered search features, and reveals the profound reshaping of how users discover and consume content online. By the end of this report, you’ll understand where and why organic visibility is collapsing in 2025, which industries are hit hardest, and what data-backed strategies leading publishers and SaaS brands are using to recover growth. You’ll see which channels still deliver ROI, how AI Overviews reshape user behavior, and how to pivot your SEO and content strategy for resilience in the zero-click era.
Executive summary: The Great Decoupling & Key Findings
TL;DR:
60% of Google searches are zero-click; mobile at 77%.
AI Overviews appear for 13% of queries; CTR drops 47%.
Major losses: HubSpot (-70–80%), CNN (-27–38%).
Winners: People.com (+27%), Men’s Journal (+415%).
Strategies: focus on AI citations, deep expertise, multi-platform presence, revenue over traffic.
Organic traffic in 2025 is experiencing what industry analysts call “The Great Decoupling”—a phenomenon where search engine usage continues to rise while clicks to websites decline dramatically. This research, compiled from industry reports, publisher data, and academic studies, reveals that 60% of Google searches now end without any click to a website, up from 58% in 2024. The median publisher experienced a 10% year-over-year traffic decline in the first half of 2025, with news publishers down 7% and non-news content sites down 14%.
The data presents a stark reality: while Google processes between 9.1 and 13.6 billion searches daily—significantly more than the 8.5 billion in 2024—fewer of those searches result in website visits. This paradox stems primarily from Google’s aggressive rollout of AI Overviews, which now appear for 13.14% of all queries, more than doubling from 6.49% in January 2025. When AI Overviews are present, click-through rates plummet to just 8%, compared to 15% for traditional search results without AI summaries.
| Metric | 2024 Baseline | 2025 H1 Average | Change | Implication (per Warehouse Leak) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily Google Searches | 8.5B | 9.1-13.6B | +7-60% | Volume up, but zero-clicks capture 60% via AI summaries. |
| Zero-Click Rate | 58% | 60% | +3.4% | Mobile at 77%; erodes NavBoost for low-engagement sites. |
| AI Overview Appearance Rate | 6.49% | 13.14% | +102% | Triggers on informational queries (88%); demands E-E-A-T proof. |
| CTR with AI Overviews | 15% | 8% | -47% | Cited sources clicked only 1%; prioritize siteAuthority for visibility. |
Publisher impact — winners and losers quantified
News publishers: case studies & median declines
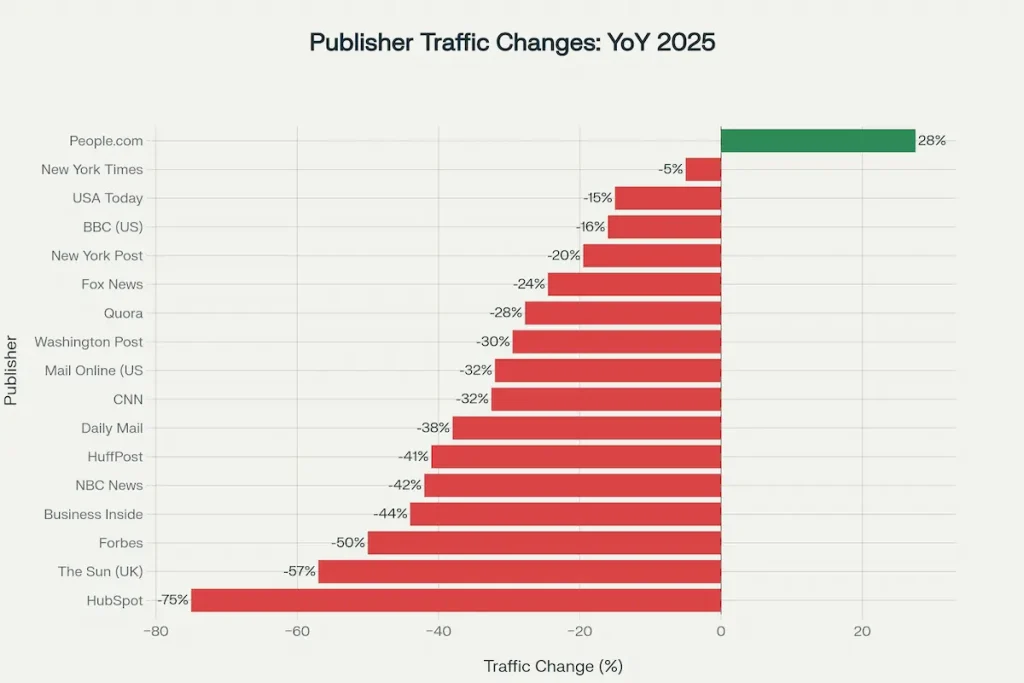
The traffic erosion has been particularly devastating for news publishers and established content brands. Analysis of the top 50 U.S. news websites reveals that 37 sites experienced year-over-year traffic declines in May 2025, with only 13 showing growth. CNN suffered one of the steepest drops, with traffic declining between 27% and 38% year-over-year depending on the measurement period. The network’s visits fell from approximately 440 million in 2024 to around 311-323 million by mid-2025.
Business news outlets faced similarly dramatic losses. Forbes experienced a 50% traffic decline year-over-year in July 2025. Business Insider saw traffic drop between 40% and 48%, with some analysts from Loopex Digital reporting the highest decline at 48.4%. The Huffington Post declined 40-42%, while NBC News dropped 42%. Even legacy publishers weren’t spared—The Washington Post experienced declines ranging from 19% to 40% depending on the time period measured.
British publications serving the U.S. market experienced particularly severe losses. The Sun (UK) saw traffic plunge 55-59% year-over-year, while the Daily Mail’s U.S. operation (Mail Online) declined 32-44%. The New York Post, owned by News Corp, experienced a 12% decline according to ComScore data, dropping from over 433 million visits to 381 million.
HubSpot case study: lessons for B2B SaaS
Perhaps no single example has generated more discussion in the digital marketing community than HubSpot’s catastrophic traffic loss. The marketing automation platform, long considered an SEO leader, experienced a 70-80% decline in organic traffic between 2024 and 2025. According to Ahrefs data widely circulated (and subsequently deleted) in early 2025, HubSpot’s monthly organic visits plummeted from approximately 13.5 million in November 2024 to less than 7 million by December 2024—and continued declining to as low as 6 million in subsequent months.
The scale of HubSpot’s decline sent shockwaves through the content marketing industry precisely because of the company’s reputation. As one industry analyst noted on LinkedIn, “If HubSpot, with one of the best SEO teams in the world, can experience this, none of us are safe”. HubSpot’s CEO Yamini Rangan acknowledged the shift on the company’s quarterly earnings call, stating that organic search traffic is “declining globally” and that “AI overviews are giving answers, and fewer people are clicking through to websites”.
Multiple analyses identified the primary causes of HubSpot’s traffic loss. The company had built its strategy on top-of-funnel content targeting broad, high-traffic keywords with minimal connection to its core CRM platform. Pages about “famous sales quotes,” “cover letter examples,” “resignation letter examples,” and “real estate licenses” drove significant traffic but had little relevance to HubSpot’s actual offerings. When Google’s March 2024 algorithm update prioritized content closely tied to a website’s core expertise, HubSpot’s loosely related content was systematically devalued.
HubSpot’s response has been instructive. The company now reports that just 10% of leads come from blog traffic, down from what was once the majority of their pipeline. They’ve pivoted to optimize for AI search citations, claiming to be “cited in LLMs more than any other CRM” and achieving conversions from this channel. For a deeper dive into this paradigm shift, explore our 2025 AI citation and LLM visibility report which comprehensively outlines the new rules of digital visibility. This strategic shift from traffic acquisition to visibility within AI responses represents the new reality many publishers face.
Entertainment and niche winners — why some grew
Not every content category experienced decline. People.com emerged as a notable winner, posting a 27.52% year-over-year traffic increase through September 2025. The entertainment news site’s visual-heavy content and celebrity focus appear less susceptible to AI summarization than text-based informational content. Similarly, Men’s Journal quadrupled its traffic year-over-year in May 2025, up 415%. The Cooldown.com grew 96%, and India Times increased 77%.
Substack, the newsletter platform, demonstrated 40% year-over-year growth in July 2025, rising to the 19th most-visited news website in the U.S. with 67.7 million visits. This growth reflects users seeking authentic voices and first-hand perspectives—content types that Google’s Liz Reid specifically identified as gaining traffic in the AI era.
The Zero-Click Search Phenomenon: Users Find Answers Without Leaving Google
TL;DR:
Trend: 60% searches end without click; mobile leads at 77%.
Geography: US ~58.5%, EU/UK ~59.7%.
Drivers: AI Overviews, voice assistants, mobile-first usage.
Implication: Users get answers without visiting sites → CTR declines.
The Accelerating Trend Toward No-Click Results
The fundamental driver of traffic decline is the explosive growth of “zero-click searches”—queries where users obtain their answer directly from the search results page without clicking any website. Research from SparkToro and Similarweb tracking this phenomenon since 2017 shows a clear upward trajectory. Zero-click searches represented 54.11% of queries in 2017, dipped briefly to 50% in 2019, then climbed steadily to 62.41% by 2021. After what appears to be a measurement methodology change that temporarily suppressed the figure to 26% in 2022, zero-click searches have stabilized at approximately 60% in 2024-2025.
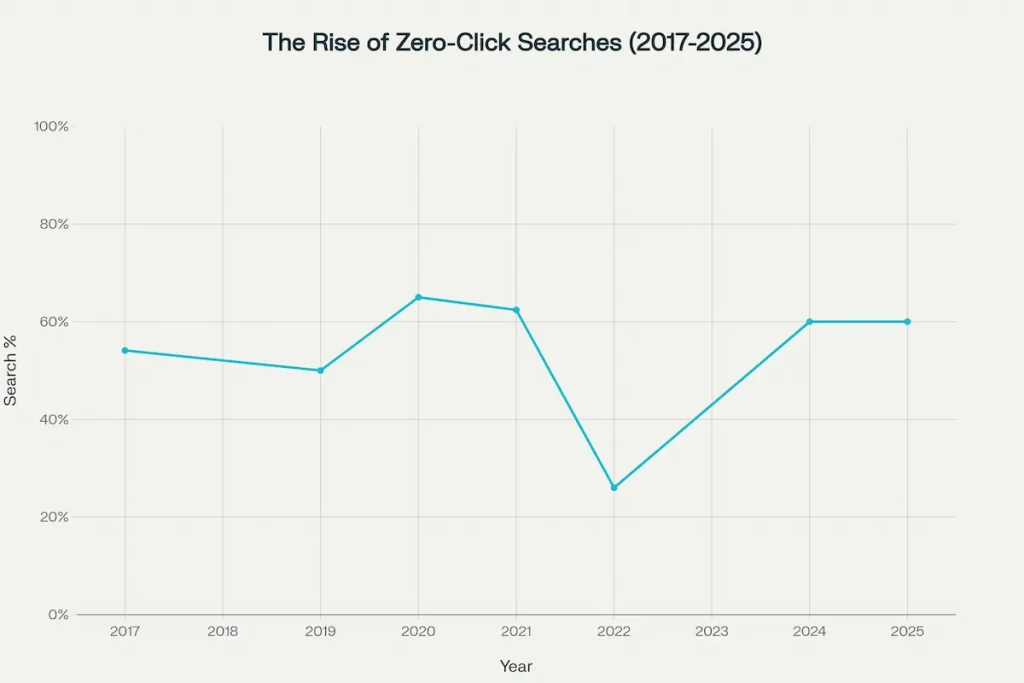
Recent data from multiple sources confirms this 60% baseline figure. A Bain & Company study found that 80% of consumers now rely on zero-click results in at least 40% of their searches. For news-related queries specifically, Similarweb reported that the proportion of searches ending without a click rose from 56% in 2024 to 69% by May 2025. This 13-percentage-point increase in just one year represents one of the most rapid shifts in user behavior ever documented in search.
The zero-click phenomenon varies significantly by device type. Mobile searches demonstrate far higher zero-click rates at 77.2%, while desktop searches end without clicks 46.5% of the time. This disparity reflects both the prominence of SERP features on smaller mobile screens and user behavior differences—mobile users often seek quick answers while on the go, while desktop users more frequently engage in research requiring multiple sources.
Geographic Variations in Zero-Click Behavior
Zero-click rates also vary by geography. U.S. searches end without clicks 58.5% of the time, while European Union and UK searches show a slightly higher rate at 59.7%. These relatively small differences suggest the phenomenon is global rather than region-specific, driven by universal changes in search engine design rather than local user preferences.
Current statistics significantly undercount the true prevalence of zero-click searches because they exclude voice answers delivered through Google Assistant and searches conducted within Google’s mobile app, both of which rarely generate website clicks. If these were included, the actual zero-click rate would likely exceed 70%.
| Device/Geography | Zero-Click Rate | YoY Change | NavBoost Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile (Global) | 77.2% | +4% | Quick-answer bias; optimize for featured snippets. |
| Desktop (Global) | 46.5% | +2% | Research mode; deeper content wins residual clicks. |
| U.S. | 58.5% | +3% | Stable; focus on E-E-A-T for trust. |
| EU/UK | 59.7% | +3.5% | Higher; regulatory scrutiny may slow AI rollout. |
AI Overviews: The Primary Accelerant of Traffic Decline
TL;DR:
Launch: May 2024, aggressive rollout
Coverage: 13% of queries; 88% informational queries
CTR: Drops 47% when AI summary present (8% vs 15% w/o)
Industry Impact:
Real Estate +258%, Restaurants +273%, Retail +206% (high vulnerability)
Health, Science: moderate impact due to E-E-A-T barriers
Publisher Insight: Only 1% click through AI-cited sources.
Rapid Expansion of AI-Generated Summaries
Google officially launched AI Overviews in May 2024, though the feature began as the “Search Generative Experience” in May 2023. The rollout has been aggressive. In January 2025, AI Overviews appeared for 6.49% of queries. By March 2025, this had more than doubled to 13.14%—a 102% increase in just two months. The trajectory suggests AI Overviews could appear for 20-25% of queries by the end of 2025 if current growth rates continue.
Research from Semrush analyzing over 10 million keywords found that 88.1% of queries triggering AI Overviews are informational in nature. This concentration on informational queries has devastating implications for educational content, news publishers, and how-to guides—precisely the content types that have traditionally driven the most organic traffic.
The expansion varies dramatically by industry vertical. Between January and March 2025, certain categories experienced explosive growth in AI Overview appearances. Real estate saw a 258% increase in keywords triggering AI Overviews, the largest two-month leap of any industry. Transportation jumped 223%, restaurants increased 273%, and retail grew 206%. Science-related queries showed a 22.27% increase in AI Overview share, while health queries grew 20.33%, people & society increased 18.83%, and law & government rose 15.18%.
| Vertical | AI Overview Growth (Jan-Mar 2025) | Vulnerability to Traffic Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Real Estate | +258% | High; users accept summaries over site visits. |
| Restaurants/Retail | +273%/206% | Medium; visuals mitigate some loss. |
| Health/Science | +20%/22% | Low; E-E-A-T barriers protect expert content. |
These industry-specific surges reveal Google’s strategic rollout pattern. High-trust, information-dense categories where users seek authoritative answers are being prioritized for AI treatment. Notably, navigational queries (where users seek a specific website) that trigger AI Overviews doubled from 0.74% in January to 1.43% by March 2025, suggesting Google is expanding AI Overviews beyond pure information seeking.
The Devastating Impact on Click-Through Rates
The most comprehensive academic study of AI Overviews’ impact on traffic comes from the Pew Research Center, which conducted a controlled analysis in March 2025 using 900 participants. The findings are unequivocal: searches displaying AI Overviews saw click-through rates plummet to just 8%, compared to 15% for traditional search results without AI summaries. This represents a 47% reduction in clicks when AI Overviews are present.
Even more concerning for publishers, users almost never click on the sources cited within AI Overviews themselves. Pew found that only 1% of AI Overviews led to a click on a cited source. The most commonly cited sources—Wikipedia, YouTube, and Reddit, which together represent 15% of all AI-sourced information—capture the rare clicks that do occur, further disadvantaging traditional publishers.
Industry studies corroborate these findings. Advanced Web Ranking data analyzed by multiple sources showed that click-through rates for keywords without AI Overviews saw slight improvements, while those with AI Overviews experienced declining CTRs over the past year. Seer Interactive’s research demonstrated the same divergence. The Professional Publishers Association in the UK documented click-through rate declines of 10-25% year-over-year despite stable or improving rankings, with specific examples including a lifestyle publisher whose CTR dropped from 5.1% to 0.6% and an automotive publisher whose CTR fell from 2.75% to 1.71%.
Publisher Data Contradicts Google’s Claims
The data on AI Overviews’ impact has created a public dispute between publishers and Google. In August 2025, Google VP and Head of Search Liz Reid published a blog post claiming that “total organic click volume from its search engine to websites has been ‘relatively stable’ year-over-year” and that “average click quality has slightly increased”. Reid asserted that “third-party reports that inaccurately suggest dramatic declines in aggregate traffic” are based on “flawed methodologies, isolated examples, or traffic changes that occurred prior to the roll out of AI features in Search”.
Publishers immediately challenged Google’s characterization. Digital Content Next (DCN), representing approximately 40 premium publishers including The New York Times, Condé Nast, and Vox, released detailed data from 19 member companies covering May and June 2025. The DCN study found that median year-over-year referral traffic from Google Search declined 10%, with news brands down 7% and non-news brands down 14%. Over the eight-week study period, “the median Google Search referral was down almost every week, with losses outpacing gains two-to-one”.
DCN CEO Jason Kint emphasized that publishers in the survey directly attributed these losses to AI Overviews, stating the data offers “ground truth” of what’s actually happening, cutting through Google’s vague claims about “quality clicks”. A separate study by the UK’s Professional Publishers Association found similar patterns, with evidence showing “click-through rates falling 10-25% year-over-year despite stable rankings”.
The Reporting Anomaly: September 2025 Search Console Changes
TL;DR:
Google removed
&num=100parameter in Sept 2025 → Search Console impressions ↓Effect: Revealed actual human traffic; bot-inflated impressions removed
Actionable Advice: Use Analytics for real traffic, not just Search Console.
The num=100 Parameter Elimination
Adding complexity to traffic analysis, Google made significant changes to Search Console reporting in mid-September 2025 that created confusion about whether traffic losses were real or measurement artifacts. For years, Google allowed the &num=100 parameter in search URLs, which enabled users and rank-tracking tools to see 100 results per page instead of the default 10. This parameter was heavily used by large language model (LLM) bots crawling search results to train AI systems, as well as by SEO tools tracking keyword positions.
In September 2025, Google disabled this functionality, implementing paginated results with near-infinite scroll instead. This change had two immediate effects. First, it dramatically increased the cost and difficulty of scraping search results, as bots now needed to send ten times as many requests to gather the same data. Second, and more importantly for publishers, it filtered out the “inflated impressions” these bots had been generating in Search Console.
For years, bot traffic from AI scrapers and rank-tracking tools had appeared as impressions in Search Console, even though no human ever saw those results. When a page ranked on page 5 or 10, bots loading those results created thousands of impression counts that made visibility appear higher than it actually was. The September update removed these bot impressions, revealing actual human-only visibility for the first time.
Distinguishing Real Decline from Measurement Changes
The result was mass confusion among website owners who saw impression counts “fall off a cliff” in mid-September. Many initially feared a massive deranking or penalty. In reality, two distinct phenomena were occurring simultaneously. First, impression counts were dropping due to the elimination of bot traffic from reporting—a measurement change, not a real traffic change. Second, actual organic traffic was genuinely declining due to AI Overviews and zero-click searches—a real traffic change that had been occurring throughout 2025.
To distinguish between these effects, SEO experts recommended comparing actual traffic metrics (users, sessions, pageviews) from Google Analytics or other analytics platforms rather than relying solely on Search Console impressions. If Analytics showed stable traffic while Search Console impressions dropped, the issue was primarily the reporting change. If both Analytics and Search Console showed declines, real traffic loss was occurring.
This reporting confusion coincided with the Google June 2025 Broad Core Update that launched June 30, 2025 and took approximately three weeks to roll out. Some sites experienced volatility during this period, though many observers noted that ranking fluctuations were less severe than the ongoing traffic decline from AI Overviews.
Industry-Specific Impacts: Who’s Hit Hardest and Why
TL;DR:
News: Most informational queries → high AI coverage → median -7% traffic
Health, Science, Education: High AI Overview penetration → existential threat to how-to guides
B2B / SaaS: Vulnerable if content is generic; success with niche, expert content
E-commerce: Transactional queries partially protected; commercial intent content increasingly summarized
Local Search: AI Overview coverage up 200–270% for restaurants, real estate, transportation; conversion may still be strong
News Publishers: Information Queries Under Siege
News publishers face particularly acute challenges because their content overwhelmingly serves informational intent—precisely the query type most likely to trigger AI Overviews. The DCN study found news brands experienced a 7% median traffic decline, which while notable, was actually less severe than the 14% decline for non-news content brands. This relative resilience may reflect news content’s timeliness advantage—breaking news and recent events are harder for AI to summarize without current sources.
However, the overall trajectory for news is deeply concerning. Analysis from Press Gazette tracking the top 50 U.S. news websites month-by-month throughout 2025 reveals sustained losses. In May 2025, only 15 of 50 grew traffic year-over-year. By July 2025, only 6 of 50 showed growth. Major news organizations saw compounding losses: CNN declined from 351 million visits in March to 323 million in July (8% decline in four months), while Fox News dropped from 272.8 million to 249 million (9% decline).
The concentration of traffic among the largest news brands is intensifying. The New York Times, CNN, and Fox News together account for over 1 billion monthly visits, while mid-tier publishers struggle. This winner-take-most dynamic suggests that brand strength and direct navigation are becoming more important than organic discovery as AI Overviews displace traditional search results.
Health, Science, and Educational Content: High AI Overview Penetration
Content in health, science, education, and legal categories faces extraordinarily high rates of AI Overview appearance because these topics involve complex information that users want simplified. Semrush data shows these verticals experienced the highest growth in AI Overview keyword triggers between January and March 2025: science (+22.27%), health (+20.33%), people & society (+18.83%), and law & government (+15.18%).
For educational platforms and how-to content, this creates an existential challenge. When users search “how to change a tire” or “what are the symptoms of diabetes,” AI Overviews now provide step-by-step instructions or symptom lists directly on the SERP. The comprehensive answer eliminates the need to visit the websites that originally created this content, effectively turning publisher investments into training data for Google’s AI with no reciprocal traffic benefit.
Marketing and SaaS: HubSpot’s Warning to B2B Tech
The HubSpot case demonstrates the vulnerability of B2B marketing and SaaS content. Beyond HubSpot’s specific missteps with irrelevant content, the broader challenge for B2B tech companies is that much of their traffic historically came from educational content about general business topics rather than product-specific searches. Terms like “marketing strategy,” “sales techniques,” “project management tips”—the bread and butter of B2B content marketing—are precisely the informational queries most vulnerable to AI summarization.
A B2B SaaS startup case study from Bruce Clay illustrates an alternative path. Despite operating in an emerging tech market, the company achieved a 367% increase in organic traffic in 17 months through laser-focused, industry-specific content that positioned them as authorities in their niche. The key was creating glossary pages, tutorials, and blog posts that required deep expertise rather than general business advice that AI could easily replicate.
E-Commerce and Product Searches: An Evolving Battleground
E-commerce presents a more complex picture. While informational content like “best running shoes for flat feet” increasingly receives AI Overview treatment, transactional queries where users intend to purchase remain relatively protected. Google has business incentives to maintain Shopping ads and product listings that generate revenue, creating a natural limit on how much e-commerce traffic AI can capture.
However, the expansion of AI Overviews to more commercial intent is visible in the data. Retail keywords triggering AI Overviews increased 206% between January and March 2025. For product research queries, AI Overviews increasingly provide comparison information, specifications, and feature explanations that previously required visiting multiple product pages. This “pre-education” means users arrive at e-commerce sites later in their journey—if they arrive at all—having already narrowed choices through AI summaries.
Local Search: Restaurants, Real Estate, Transportation
Local intent queries are experiencing dramatic increases in AI Overview coverage, though the traffic impact remains somewhat unclear. Restaurants saw a 273% increase in keywords triggering AI Overviews, real estate grew 258%, and transportation increased 223% between January and March 2025. These high growth rates suggest Google is aggressively deploying AI for local questions like “best Italian restaurants near me” or “homes for sale in Austin under $400k.”
However, local searches often require current information (hours, availability, pricing) and culminate in actions (reservations, showings, bookings) that AI summaries can facilitate but not complete. Google’s integration of local business data into AI Overviews may actually increase conversion efficiency for local businesses if users arrive more informed and purchase-ready, even if impression counts decline. The net traffic and revenue impact for local businesses remains an area requiring further study as 2025 progresses.
The Positive Counter-Narrative: Search Volume Growth and SEO Success
TL;DR:
Total Search Volume: 9.1–13.6B/day ↑ (growing faster than zero-clicks)
SEO ROI: Organic traffic still 53% of website traffic; 5x more cost-effective than paid ads
CTR & Rankings: Top positions capture majority of clicks; featured snippets 42.9% CTR
Conversion: SEO leads convert 8.5x better than outbound; revenue per visitor higher than paid traffic
Total Search Volume Continues Rising
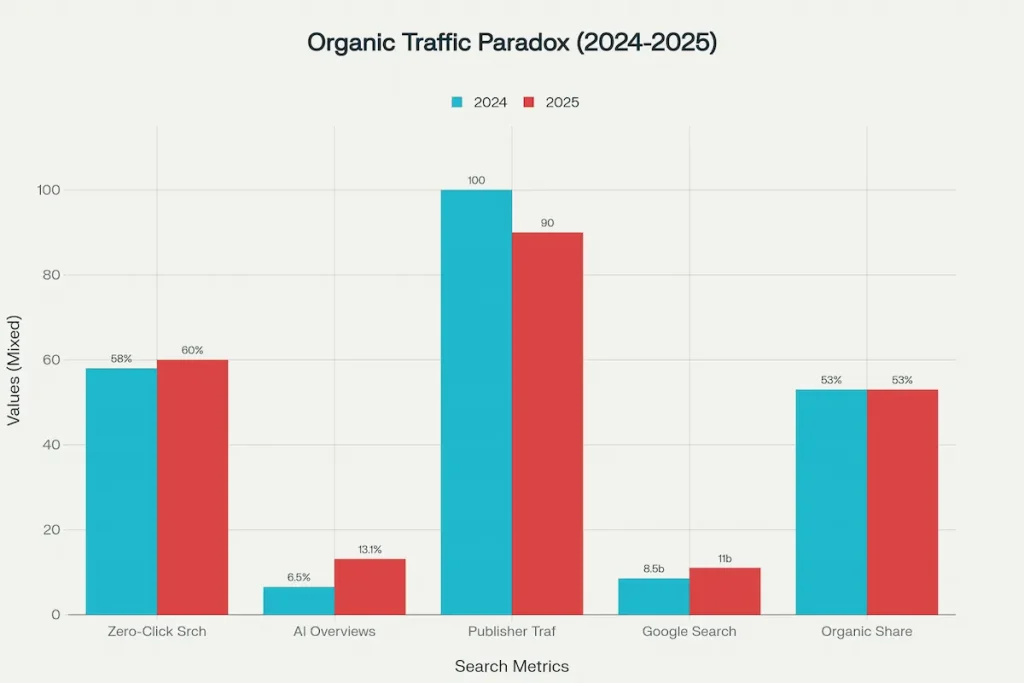
Despite the traffic apocalypse for many publishers, search as a behavior remains extraordinarily healthy. Google processes an estimated 9.1 to 13.6 billion searches per day in 2025, up from 8.5 billion in 2024. This represents over 5 trillion searches annually. Even as AI chatbots like ChatGPT gain adoption (processing approximately 3 billion prompts per month), Google remains dominant with over 89% of the search engine market.
The growth in search volume creates what analysts call “the organic traffic paradox”. Even though the percentage of searches ending in zero clicks has increased, the absolute number of searches has grown faster, resulting in more total clicks to websites than in previous years. Without specific zero-click marketing strategies, businesses risk losing visibility entirely as search engines prioritize direct answers. Neil Patel Digital’s analysis of 30,000 websites found that overall organic traffic increased despite the prevalence of AI Overviews. The key insight: while individual sites may lose traffic, the total pool of available clicks has actually expanded because search volume growth outpaces zero-click growth.
SEO Effectiveness Remains High for Quality Content
Survey data from practitioners shows continued confidence in SEO’s effectiveness when properly executed. Conductor’s 2025 State of SEO Survey found that 91% of respondents reported that SEO positively impacted website performance and marketing goals in 2024. On average, organic search produced 33% of overall website traffic across seven key industries in 2024, maintaining its position as the single largest traffic source for most businesses.
Multiple SEO case studies from 2025 demonstrate that well-executed strategies still deliver exceptional results. Flyhomes, a real estate platform, achieved 10,737% traffic growth in 3 months by expanding from 10,000 to 425,000 pages focused on cost-of-living guides, which generated 55.5% of all site traffic. Brainly, an education platform, tripled keyword rankings year-over-year through user-generated content that created over 2 million question landing pages. A regional dental provider increased organic traffic by 140% year-over-year, allowing them to completely turn off paid search advertising.
The CBD Supplier, operating in a highly competitive industry, grew search traffic by 557% in 12 months through long-tail keyword targeting and internal linking optimization. CMA Exam Academy saw 125% revenue growth with 147% more users and 121% increased pageviews through technical SEO improvements and content optimization. These success stories share common elements: deep specialization, strong technical foundations, and content that demonstrates genuine expertise rather than generic information.
Rankings Still Matter: CTR Data Shows Value of Top Positions
For queries without AI Overviews, traditional ranking factors remain powerful. Advanced Web Ranking data shows the average #1 ranking on Google receives 27.6% of all clicks, while the top 3 results collectively capture 54.4% of clicks. Featured snippets in position zero achieve an impressive 42.9% click-through rate, actually exceeding the standard first organic result’s 39.8% CTR.
In fact, in 2025, the #1 organic result on Google now enjoys a 39.8% CTR, up from 39.6% the previous year. The second position saw a similar improvement. For searches without AI Overviews, click-through rates have actually increased as Google continues to refine the relevance of top results. This suggests that for queries where AI doesn’t provide complete answers, ranking excellence matters more than ever.
Organic Search Conversion Rates Remain Superior
From a business perspective, organic search continues to deliver exceptional return on investment compared to other channels. Organic search accounts for 53.3% of all website traffic, making it 5x more cost-effective than paid advertising when accounting for long-term value. While AI Overviews reduce clicks initially, they often generate higher-quality traffic from users with specific intent who weren’t satisfied with the AI summary.
Organic traffic conversion rates typically deliver between 2.7% to 3.75%, often outperforming paid search in many industries. SEO leads close at 14.6% compared to 1.7% for outbound leads, making SEO-generated leads 8.5 times more likely to convert. For B2B businesses specifically, organic search drives 44.6% of all revenue—more than twice as much as all other digital channels combined.
These conversion metrics explain why despite traffic declines, many businesses continue investing heavily in SEO. Revenue per organic visitor often exceeds revenue per paid visitor because organic visitors demonstrate higher intent and trust. As one analysis noted, “While the percentage of zero-click searches has increased, users coming from organic search convert better because they’re actively seeking solutions rather than being interrupted with ads”.
Adaptation Strategies: How Publishers Are Responding
TL;DR:
AI Citation Focus: Structured data, schema, E-E-A-T, case studies, testimonials
Content Depth: Proprietary research, original insights, first-hand experience
Diversification: TikTok, YouTube, LinkedIn, Reddit, email, alternative search engines
Video Content: Resistant to AI summarization, high engagement
Revenue Focus: Measure conversions, optimize user experience, maximize lifetime value
Optimizing for AI Citations Rather Than Traffic
The most fundamental strategic shift involves changing success metrics from traffic to visibility. As HubSpot’s CEO articulated, companies must now focus on being “cited in LLMs more than any other [competitor]” and driving conversions from AI citations rather than traditional website visits. This represents a philosophical change: accepting that users may never visit your website while still achieving business objectives through brand awareness and authority building within AI responses.
To optimize for AI citations, publishers are implementing structured data markup more comprehensively than ever. Schema.org markup helps AI systems understand content structure, authorship, and relationships between topics. Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals have intensified in importance, with Google’s March 2024 update penalizing 87% of YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) sites lacking first-hand expertise.
Demonstrating real experience has become critical. This means documenting case studies with measurable outcomes, including behind-the-scenes content showing your process, adding detailed author bylines with relevant credentials, and showcasing user-generated content and testimonials. The goal is becoming a source that AI systems trust and cite, even if users never click through.
Content Depth and Differentiation
Surface-level content that AI can easily summarize has lost nearly all value. The strategic response is creating content with depth that requires human expertise and cannot be replicated by AI summaries. This includes comprehensive guides with proprietary research, original data and industry insights, detailed case studies with specific outcomes, and content that showcases unique perspectives rather than rehashed information.
Multiple industry observers noted that “AI content will advance and become less formulaic, but there will always be demand for high-quality, differentiated content that showcases unique and creative human perspectives”. As AI content proliferates, authentic voice and first-hand experience become differentiators. Publishers are investing in subject matter experts (SMEs) who can provide insights AI cannot replicate.
Diversification Beyond Google Search
Recognition that Google organic search can no longer be a primary traffic source is driving diversification strategies. Successful publishers are building presence across multiple discovery platforms: TikTok’s search function for video content discovery, Instagram’s search capabilities for visual content, LinkedIn for B2B thought leadership, Reddit and online communities for authentic conversation, email and newsletter direct relationships with audiences, and alternative search engines like Perplexity and ChatGPT.
Community engagement is emerging as particularly important. As one SEO strategist advised, “For B2B and ecommerce/B2C, engaging with communities will become a crucial growth strategy”. Building relationships in forums, social platforms, and niche communities creates traffic sources that AI cannot easily disintermediate. Direct relationships via email lists provide owned channels independent of algorithmic changes.
Video Content as AI-Resistant Format
Video continues to offer differentiation opportunities because AI has made slower advances in this medium compared to text. “Video continues to offer a unique opportunity to differentiate, as AI has yet to make significant advances in this medium,” noted one analysis. Brands focusing on high-quality video strategically deployed across platforms like TikTok, YouTube, and LinkedIn are experiencing strong engagement in 2025.
The persistence of YouTube (owned by Google) as the second-largest search engine globally, and its relative insulation from zero-click dynamics, makes video content particularly valuable. Users searching YouTube expect to watch videos, creating a different dynamic than text-based searches where AI summaries can provide complete answers.
Revenue Focus Over Traffic Metrics
Perhaps the most important strategic adaptation is shifting from traffic-based to revenue-based success metrics. A survey of 3,000 businesses revealed that while most experienced organic traffic declines in 2025, companies that maintained or grew revenue shared two characteristics: an omnichannel approach creating seamless customer experiences across multiple touchpoints, and a strong focus on conversion rate optimization turning existing traffic into paying customers regardless of volume.
The findings underscore “a vital strategic shift for businesses operating online. Relying solely on organic search traffic is no longer viable”. Publishers who excel at converting visitors—regardless of traffic source or volume—demonstrated far greater revenue resilience than those focused purely on traffic acquisition. This means investing in user experience, persuasive content, clear value propositions, streamlined conversion paths, and retention strategies that maximize customer lifetime value.
Future Outlook: Predictions Through Late 2025 and Beyond
TL;DR:
AI Overview Expansion: Expected 20–25% coverage by end of 2025
Zero-Click Rate: Could approach 70%
Publisher Consolidation: Weak brands may close or be acquired
Platform Diversification: Mandatory for survival; content must be platform-native
AI-First Content Discovery: Potential future monetization via LLM licensing or citation-based revenue
Continued AI Overview Expansion
All indicators suggest AI Overviews will continue aggressive expansion through the remainder of 2025 and into 2026. If the January-to-March growth rate of 102% continued linearly, AI Overviews would appear for 20-25% of all queries by year-end 2025. Even if growth moderates, reaching 18-20% coverage by December appears probable. Google’s business incentive is clear: keeping users on Google properties increases opportunities to serve ads and collect data.
The expansion will likely prioritize additional commercial intent queries where Google can monetize through Shopping ads alongside AI summaries. Navigational queries will increasingly receive AI treatment, though brand protection considerations may limit how aggressively Google summarizes well-known company information. The technical infrastructure for AI Overviews has matured rapidly, removing scaling constraints that existed in early 2024.
Zero-Click Rate Approaching 70%
Multiple analysts predict zero-click searches will continue rising toward 70% of all queries by late 2025 or early 2026. The current 60% baseline combined with AI Overview expansion makes this trajectory plausible. However, certain query types will always generate clicks: transactional searches where users intend to purchase, navigational searches for specific websites, local searches requiring current information like hours or menus, and research queries requiring multiple sources.
The plateauing effect observed in 2024-2025 (holding near 60% rather than continuing exponential growth) suggests user behavior creates natural limits. Users frustrated by AI inaccuracies or needing more depth than summaries provide will continue clicking. The question for publishers is whether they can maintain business viability capturing 30-40% of searches rather than the 50-60% accessible in previous years.
Publisher Consolidation and Business Model Shifts
The traffic declines documented throughout 2025 will inevitably force business model innovation and market consolidation. Publishers overly dependent on SEO traffic without diversified audience development strategies face existential challenges. Subscription and membership models that create direct reader relationships become more attractive when organic discovery weakens. Sponsorship and partnership revenue models that don’t depend on traffic volume gain appeal.
We should expect continued consolidation among news publishers, with weaker brands closing or being acquired by larger entities with more resources to adapt. The gap between winners and losers will widen—publications with strong brands, direct audiences, and differentiated content will maintain viability, while undifferentiated content farms dependent on SEO will struggle. The “middle tier” of publishers—large enough to have substantial costs but not large enough to have brand power—faces particular pressure.
Platform Diversification Becoming Mandatory
The successful content businesses of 2026 will look markedly different from those of 2023. Multi-platform presence will shift from optional to mandatory. Publishers must master content formats optimized for each platform: short-form video for TikTok and Instagram, longer educational content for YouTube, conversation-oriented posts for LinkedIn and X, visual design for Pinterest, and newsletter formats for email and Substack.
This requires structural changes in content operations—moving from “publish once on website, promote everywhere” to “create natively for each platform where audiences congregate.” The implications for staffing, workflow, and skills are profound. Content strategists must become platform strategists, understanding discovery algorithms and audience behaviors across multiple ecosystems rather than just Google organic search.
AI-First Content Discovery Models
Looking further ahead, the next generation of content discovery may bypass traditional websites entirely in favor of AI-mediated experiences. Large language models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity are evolving toward being primary research assistants rather than supplementary tools. While ChatGPT currently receives approximately 3 billion prompts per month—far less than Google’s daily 9-13 billion searches—the growth trajectory is steep.
For content creators, this raises profound questions about sustainable business models. If AI systems synthesize information from multiple sources to answer user questions without directing traffic to original publishers, how do publishers capture value? Potential models include API-based licensing where LLMs pay for content access, citation systems with revenue sharing similar to YouTube monetization, and premium membership tiers with exclusive content not available to AI scrapers.
The resolution of these business model questions will determine whether independent digital publishing remains viable or becomes unsustainable, forcing consolidation toward a small number of large brands capable of capturing attention through channels other than organic search.
TL;DR:
Organic traffic is declining but search remains robust → opportunity in strategic adaptation.
High-quality, differentiated content and AI citation optimization are crucial.
Revenue-focused metrics outperform traffic-focused strategies.
Platform diversification and video adoption increase resilience.
Publishers must prepare for AI-first discovery models to remain viable.
The data compiled throughout this analysis paints a clear picture: organic traffic in 2025 is experiencing its most significant disruption since the advent of modern search engines. The majority of content publishers are losing traffic, with median declines of 10% and some marquee brands experiencing 40-80% losses. Zero-click searches now dominate 60% of all queries, and AI Overviews appearing in 13% of searches cut click-through rates nearly in half.
Yet search as a behavior remains healthy and growing. Google processes billions more searches daily than in previous years. Organic search still drives 53% of all website traffic and converts at rates far superior to paid channels. The top organic positions still capture the majority of clicks for queries without AI summaries. Well-executed SEO strategies continue delivering extraordinary results for businesses with differentiated content and strong technical foundations.
The paradox resolves when we recognize this is not the death of organic search but rather its transformation. The strategies that worked in 2018—publishing moderate-quality content targeting keyword volume—no longer suffice in 2025. Success now requires genuine expertise, content depth that AI cannot replicate, multi-platform presence, optimization for AI citations alongside traditional rankings, and business models that generate value from visibility even when traffic declines.
For content publishers, the path forward demands uncomfortable choices. Accepting that many users will never visit your website while still achieving business objectives through authority and brand building. Investing resources in channels beyond Google organic search to diversify audience development. Creating dramatically higher-quality content with first-hand experience rather than optimization-focused mediocrity. Measuring success by revenue and conversions rather than traffic volume.
Those who adapt to this new reality can thrive even as traffic patterns shift. Those who continue optimizing for the SEO environment of 2020 will watch their businesses erode as AI reshapes the landscape beneath them. The data shows clearly that organic search in 2025 is not dead—but it has fundamentally changed, and only those who change with it will succeed.
References
Statistical Studies & Search Data
- How to Increase Organic Traffic (Swydo) 🔗
- Evolving SEO for 2025 (Search Engine Land) 🔗
- Future of Organic Search 2025 (TheeDigital) 🔗
- AI Overview Trigger Rates (ThemeWinter) 🔗
- Google AI Overviews Linked to 25% Drop (Slashdot) 🔗
- Zero-Click Searches 2025 (UpAndSocial) 🔗
- Semrush AI Overviews Study (Semrush) 🔗
- AI Overviews Reduce Website Clicks (ArsTechnica) 🔗
- Users Less Likely to Click With AI (Pew) 🔗
- Google Searches Per Day (ExplodingTopics) 🔗
- Search Engine Market Share (StatCounter) 🔗
- SEO Trends 2025 (Wordstream) 🔗
- 10 Key Website Traffic Metrics for 2025 (MetricsWatch) 🔗
- Zero-Click Searches Up, Organic Clicks Down (Search Engine Land) 🔗
- SEO This Year (Backlinko) 🔗
- Google Search Statistics (Notta.ai) 🔗
Editorial Analysis & Industry Reports
- Google’s Push to AI Hurts Publisher Traffic (DCN) 🔗
- Most Popular News Websites US (Press Gazette) 🔗
- Google AI Pummeling News Sites (NYPost) 🔗
- News Site Traffic Shrinking (Search Engine Land) 🔗
- Publishers Losing 25% of Traffic to AI (InFactory) 🔗
- Website Traffic Drops after AI Chats (LoopexDigital) 🔗
- Trending Publishing Websites (Semrush) 🔗
- Has AI Killed SEO? HubSpot Analysis (EdifyContent) 🔗
- HubSpot SEO Dominance (PostDigitalist) 🔗
- How HubSpot Lost SEO Organic Traffic (Taktical) 🔗
- Is SEO Dead in 2025? (Alitu) 🔗
- CNN New Primetime Low in 2025 (Editor & Publisher) 🔗
- AI Overviews SEO (BMG360) 🔗
- Traffic Apocalypse: AI Overviews (CJR) 🔗
- Zero-Click Search Redefines Marketing (Bain) 🔗
- What is Zero-Click? Turning Marketing on Its Head (Forbes) 🔗
- Notice Your Website Traffic Declining? (Thrive Agency) 🔗
- Google’s September Shake-Up (GetPassionFruit) 🔗
- Why Your Impressions Dropped (GoodFellasTech) 🔗
- Organic Traffic Growth Statistics 2025 (FireUS Marketing) 🔗
- Google AI Overview & Online Publishers (NPR) 🔗
- SEO Traffic Decline 2025 (KEO Marketing) 🔗
- Organic Traffic Growth (FZP Digital) 🔗
Market Analysis & Case Studies
- SEO Success Stories (Bruce Clay) 🔗
- SEO Case Studies (AIOSEO) 🔗
- Traffic Think Tank SEO Case Studies 🔗
- SEO Statistics (SearchAtlas) 🔗
- Top 10 SEO Case Studies in 2025 (The5Digital) 🔗
- SEO Success Stories & Case Studies (GloryWebs) 🔗
- SEO Services Success Stories (StarterStory) 🔗
- Google Search Case Studies (Google Developers) 🔗
Business, Trends & Diversification
Published Oct 30, 2025. Updated quarterly with new insights. © The Digital Bloom.

